Guest post originally published on Kiratech’s blog by Diego Braga
Krateo PlatformOps, an open-source project developed by Kiratech’s Cloud Native Dev Team, integrating Backstage, an open platform created by the Spotify IT team and now available in the CNCF Sandbox project catalog. Given the value and importance of this partneship, in the following article we want to analyze how the two platforms integrate together and their benefits.
First, what is Krateo PlatformOps?
Krateo PlatformOps is an open-source project based on a comprehensive and modular architecture to centrally create and manage any type of resource. What do we mean by that? A database, a Kubernetes cluster, a load balancer, an API gateway, a Kafka topic, a microservice template, a machine learning model, anything you can think of via standard Kubernetes APIs.
Krateo comes from the CNCF Landscape: how do I choose the best product among the wide range of open-source projects (to date, more than 900)? How do I know if the products are complementary, overlap, are mutually exclusive? Krateo will choose for you! We have gathered the best products in a single platform where you can manage them from a comprehensive dashboard and, by yourself or with our help, develop centrally adjustable templates.
The 4 winning features about Krateo in a nutshell:
- It’s installed in a secured by design Kubernetes cluster
- It’s a comprehensive stack where your resource can be built and scaled on cloud, multi-cloud, hybrid and on prem-environments
- It includes a self-service dashboard and a template list that can be integrated with custom modules
- It’s flexible and can be integrated with instruments that are already in place.
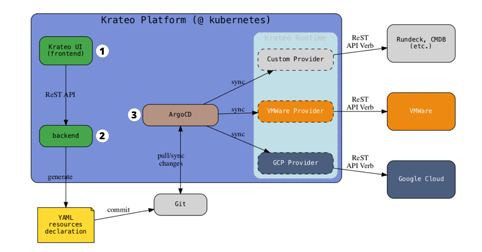
Let’s take a look at Krateo PlatformOps’ Core Architecture to completely understand how it works:
- Front-end dashboard (1): it all starts from a form to be filled with the requested fields (component name, description, owner, API url, etc) which will be passed down to the back-end
- Back-end space (2): the information will be used to fill a template and will be saved on your Git repository
- Krateo Runtime, made by:
- ArgoCD (3): the tool syncs with the Git repository and takes care of creating the resources described in the manifest files. Every change made on the git repository generates a change in resources, creating a history of every change.
What is Backstage?
Backstage is an open platform developed from Spotify’s IT team and a CNCF sandbox project that enables your team to manage its apps catalog.
It gathers all about your application in one, aggregated view: tools, services, documentation are available in a simpler development environment.
Powered by a centralized software catalog, Backstage provides a distributed system of microservices and enables your product teams to ship high-quality code quickly — without compromising autonomy. Its Software catalog allows the complete management of an application (microservices, libraries, data pipelines, websites, ML models, etc.).
It is based on YAML templates, easy to create and deploy which let you start new projects and standardize your tools already in use with the company’s best practices.
It makes it easy to create, maintain, search and use the technical documentation, by using a “docs like code” approach and it has a constantly evolving ecosystem of open-source plug-ins which let you customize and personalize even more.
How is Backstage integrated with Krateo?
Let’s see now how Krateo has integrated Backstage and what are the main benefits of this integration.
Krateo Dashboard is based on Backstage as it centralizes, through a self-service catalog, templates and properties of a service, every available documentation, the overview of the components that belong to an entire domain and all the data of the life cycle of an application.
Krateo uses the potential of the Backstage template to quickly and easily write “classic” applications, to deploy infrastructure, create DBs, etc.
Regarding Krateo’s architecture:
- In the first stage (front-end), a form must be filled with all the information about the application. The form with these values is shared with the backend which replaces the information in the template (customizing it) and put these files on a Git repository
- Subsequently Krateo Runtime, referring to the Git repository, applies the manifest on Kubernetes clusters creating pods, services, etc., while the Crossplane providers take care of generating every resource external to the cluster (databases, Kubernetes clusters and anything else).
We are therefore pleased to announce this collaboration, considering the common connection with the CNCF and with the Cloud Native world, being Kiratech CNCF Silver Member.
Start using Krateo PlatformOps! Here is the link to try the free community version.