Project post by Wenbo Qi of Dragonfly
What is Git LFS?
Git LFS (Large File Storage) is an open-source extension for Git that enables users to handle large files more efficiently in Git repositories. Git is a version control system designed primarily for text files such as source code and it can become less efficient when dealing with large binary files like audio, videos, datasets, graphics and other large assets. These files can significantly increase the size of a repository and make cloning and fetching operations slow.
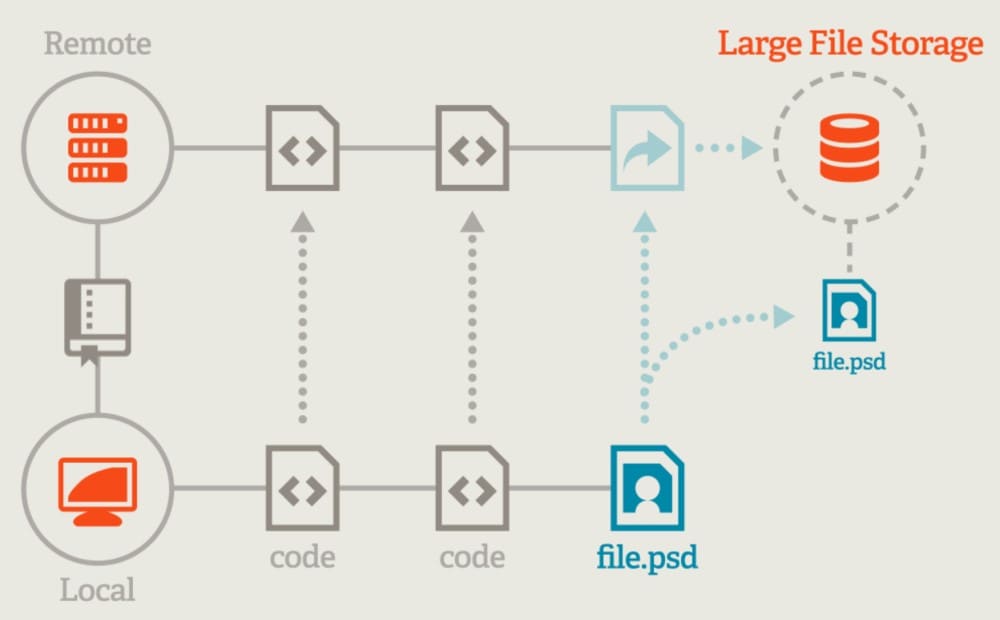
Git LFS addresses this issue by storing these large files on a separate server and replacing them in the Git repository with small placeholder files (pointers). When a user clones or pulls from the repository, Git LFS fetches the large files from the LFS server as needed rather than downloading all the large files with the initial clone of the repository. For specifications, please refer to the Git LFS Specification. The server is implemented based on the HTTP protocol, refer to Git LFS API. Usually Git LFS’s content storage uses object storage to store large files.
Git LFS Usage
Git LFS manages large files
Github and GitLab usually manage large files based on Git LFS.
- GitHub uses Git LFS refer to About Git Large File Storage.
- GitLab uses Git LFS refer to Git Large File Storage.
Git LFS manages AI models and AI datasets
Large files of models and datasets in AI are usually managed based on Git LFS. Hugging Face Hub and ModelScope Hub manage models and datasets based on Git LFS.
- Hugging Face Hub uses Git LFS refer to Getting Started with Repositories.
- ModelScope Hub uses Git LFS refer to Getting Started with ModelScope.
Hugging Face Hub’s Python Library implements Git LFS to download models and datasets. Hugging Face Hub’s Python Library distributes models and datasets to accelerate, refer to Hugging Face accelerates distribution of models and datasets based on Dragonfly.
Dragonfly eliminates the bandwidth limit of Git LFS’s content storage
This document will help you experience how to use dragonfly with Git LFS. During the downloading of large files, the file size is large and there are many services downloading the larges files at the same time. The bandwidth of the storage will reach the limit and the download will be slow.
Dragonfly can be used to eliminate the bandwidth limit of the storage through P2P technology, thereby accelerating large files downloading.
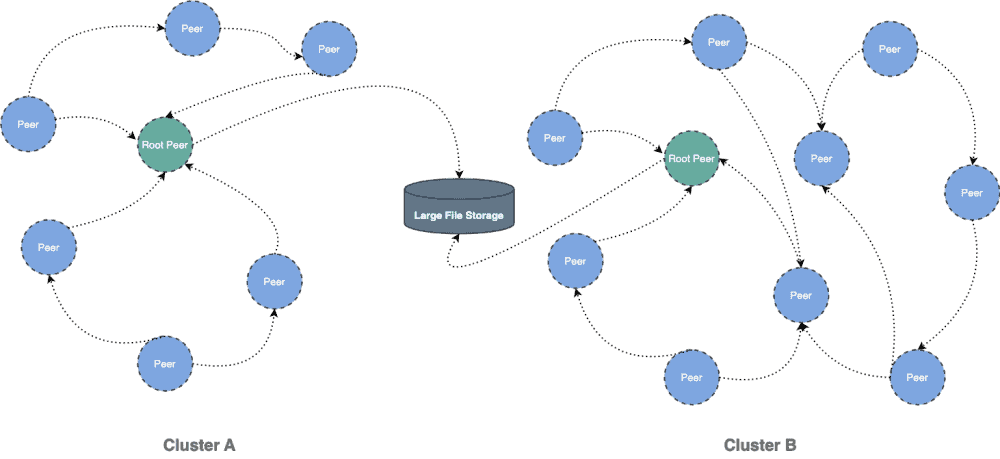
Dragonfly accelerates downloads with Git LFS
By proxying the HTTP protocol file download request of Git LFS to Dragonfly Peer Proxy, the file download traffic is forwarded to the P2P network. The following documentation is based on GitHub LFS.
Get the Content Storage address of Git LFS
Add GIT_CURL_VERBOSE=1 to print verbose logs of git clone and get the address of content storage of Git LFS.
GIT_CURL_VERBOSE=1 git clone git@github.com:{YOUR-USERNAME}/{YOUR-REPOSITORY}.git
Look for the trace git-lfs keyword in the logs and you can see the log of Git LFS download files. Pay attention to the content of actions and download in the log.
15:31:04.848308 trace git-lfs: HTTP: {"objects":[{"oid":"c036cbb7553a909f8b8877d4461924307f27ecb66cff928eeeafd569c3887e29","size":5242880,"actions":{"download":{"href":"https://github-cloud.githubusercontent.com/alambic/media/376919987/c0/36/c036cbb7553a909f8b8877d4461924307f27ecb66cff928eeeafd569c3887e29?X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Credential=AKIAIMWPLRQEC4XCWWPA%2F20231221%2Fus-east-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Date=20231221T073104Z&X-Amz-Expires=3600&X-Amz-Signature=4dc757dff0ac96eac3f0cd2eb29ca887035d3a6afba41cb10200ed0aa22812fa&15:31:04.848403 trace git-lfs: HTTP: X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&actor_id=15955374&key_id=0&repo_id=392935134&token=1","expires_at":"2023-12-21T08:31:04Z","expires_in":3600}}}]}
The download URL can be found in actions.download.href in the objects. You can find that the content storage of GitHub LFS is actually stored at github-cloud.githubusercontent.com. And query parameters include X-Amz-Algorithm, X-Amz-Credential, X-Amz-Date, X-Amz-Expires, X-Amz-Signature and X-Amz-SignedHeaders. The query parameters are AWS Authenticating Requests parameters. The keys of query parameters will be used later when configuring Dragonfly Peer Proxy.
Information about Git LFS :
- The content storage address of Git LFS is github-cloud.githubusercontent.com.
- The query parameters of the download URL include X-Amz-Algorithm, X-Amz-Credential, X-Amz-Date, X-Amz-Expires, X-Amz-Signature and X-Amz-SignedHeaders.
Installation
Prerequisites
| Name | Version | Document |
| Kubernetes cluster | 1.20+ | kubernetes.io |
| Helm | 3.8.0+ | helm.sh |
Notice: Kind is recommended if no kubernetes cluster is available for testing.
Install dragonfly
For detailed installation documentation based on kubernetes cluster, please refer to quick-start-kubernetes.
Setup kubernetes cluster
Create kind multi-node cluster configuration file kind-config.yaml, configuration content is as follows:
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
nodes:
- role: control-plane
- role: worker
extraPortMappings:
- containerPort: 30950
hostPort: 65001
- role: worker
Create a kind multi-node cluster using the configuration file:
kind create cluster --config kind-config.yaml
Switch the context of kubectl to kind cluster:
kubectl config use-context kind-kind
Kind loads dragonfly image
Pull dragonfly latest images:
docker pull dragonflyoss/scheduler:latest
docker pull dragonflyoss/manager:latest
docker pull dragonflyoss/dfdaemon:latest
Kind cluster loads dragonfly latest images:
kind load docker-image dragonflyoss/scheduler:latest
kind load docker-image dragonflyoss/manager:latest
kind load docker-image dragonflyoss/dfdaemon:latest
Create dragonfly cluster based on helm charts
Create helm charts configuration file charts-config.yaml. Add the github-cloud.githubusercontent.com rule to dfdaemon.config.proxy.proxies.regx to forward the HTTP file download of content storage of Git LFS to the P2P network. And dfdaemon.config.proxy.defaultFilter adds X-Amz-Algorithm, X-Amz-Credential, X-Amz-Date, X-Amz-Expires, X-Amz-Signature and X-Amz-SignedHeaders parameters to filter the query parameters. Dargonfly generates a unique task id based on the URL, so it is necessary to filter the query parameters to generate a unique task id. Configuration content is as follows:
scheduler:
image: dragonflyoss/scheduler
tag: latest
replicas: 1
metrics:
enable: true
config:
verbose: true
pprofPort: 18066
seedPeer:
image: dragonflyoss/dfdaemon
tag: latest
replicas: 1
metrics:
enable: true
config:
verbose: true
pprofPort: 18066
dfdaemon:
image: dragonflyoss/dfdaemon
tag: latest
metrics:
enable: true
config:
verbose: true
pprofPort: 18066
proxy:
defaultFilter: "X-Amz-Algorithm&X-Amz-Credential&X-Amz-Date&X-Amz-Expires&X-Amz-Signature&X-Amz-SignedHeaders"
security:
insecure: true
cacert: ""
cert: ""
key: ""
tcpListen:
namespace: ""
port: 65001
registryMirror:
url: https://index.docker.io
insecure: true
certs: []
direct: false
proxies:
- regx: blobs/sha256.*
- regx: github-cloud.githubusercontent.com.*
manager:
image: dragonflyoss/manager
tag: latest
replicas: 1
metrics:
enable: true
config:
verbose: true
pprofPort: 18066
jaeger:
enable: true
Create a dragonfly cluster using the configuration file:
$ helm repo add dragonfly https://dragonflyoss.github.io/helm-charts/
$ helm install --wait --create-namespace --namespace dragonfly-system dragonfly dragonfly/dragonfly -f charts-config.yaml
NAME: dragonfly
LAST DEPLOYED: Thu Dec 21 17:24:37 2023
NAMESPACE: dragonfly-system
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
1. Get the scheduler address by running these commands:
export SCHEDULER_POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace dragonfly-system -l "app=dragonfly,release=dragonfly,component=scheduler" -o jsonpath={.items[0].metadata.name})
export SCHEDULER_CONTAINER_PORT=$(kubectl get pod --namespace dragonfly-system $SCHEDULER_POD_NAME -o jsonpath="{.spec.containers[0].ports[0].containerPort}")
kubectl --namespace dragonfly-system port-forward $SCHEDULER_POD_NAME 8002:$SCHEDULER_CONTAINER_PORT
echo "Visit http://127.0.0.1:8002 to use your scheduler"
2. Get the dfdaemon port by running these commands:
export DFDAEMON_POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace dragonfly-system -l "app=dragonfly,release=dragonfly,component=dfdaemon" -o jsonpath={.items[0].metadata.name})
export DFDAEMON_CONTAINER_PORT=$(kubectl get pod --namespace dragonfly-system $DFDAEMON_POD_NAME -o jsonpath="{.spec.containers[0].ports[0].containerPort}")
You can use $DFDAEMON_CONTAINER_PORT as a proxy port in Node.
3. Configure runtime to use dragonfly:
https://d7y.io/docs/getting-started/quick-start/kubernetes/
4. Get Jaeger query URL by running these commands:
export JAEGER_QUERY_PORT=$(kubectl --namespace dragonfly-system get services dragonfly-jaeger-query -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].port}")
kubectl --namespace dragonfly-system port-forward service/dragonfly-jaeger-query 16686:$JAEGER_QUERY_PORT
echo "Visit http://127.0.0.1:16686/search?limit=20&lookback=1h&maxDuration&minDuration&service=dragonfly to query download events"
Check that dragonfly is deployed successfully:
$ kubectl get po -n dragonfly-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
dragonfly-dfdaemon-cttxz 1/1 Running 4 (116s ago) 2m51s
dragonfly-dfdaemon-k62vd 1/1 Running 4 (117s ago) 2m51s
dragonfly-jaeger-84dbfd5b56-mxpfs 1/1 Running 0 2m51s
dragonfly-manager-5c598d5754-fd9tf 1/1 Running 0 2m51s
dragonfly-mysql-0 1/1 Running 0 2m51s
dragonfly-redis-master-0 1/1 Running 0 2m51s
dragonfly-redis-replicas-0 1/1 Running 0 2m51s
dragonfly-redis-replicas-1 1/1 Running 0 106s
dragonfly-redis-replicas-2 1/1 Running 0 78s
dragonfly-scheduler-0 1/1 Running 0 2m51s
dragonfly-seed-peer-0 1/1 Running 1 (37s ago) 2m51s
Create peer service configuration file peer-service-config.yaml, configuration content is as follows:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: peer
namespace: dragonfly-system
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- name: http-65001
nodePort: 30950
port: 65001
selector:
app: dragonfly
component: dfdaemon
release: dragonfly
Create a peer service using the configuration file:
kubectl apply -f peer-service-config.yaml
Git LFS downlads large files via dragonfly
Proxy Git LFS download requests to Dragonfly Peer Proxy(http://127.0.0.1:65001) through Git configuration. Set Git configuration includes http.proxy, lfs.transfer.enablehrefrewrite and url.{YOUR-LFS-CONTENT-STORAGE}.insteadOf properties.
git config --global http.proxy http://127.0.0.1:65001
git config --global lfs.transfer.enablehrefrewrite true
git config --global url.http://github-cloud.githubusercontent.com/.insteadOf https://github-cloud.githubusercontent.com/
Forward Git LFS download requests to the P2P network via Dragonfly Peer Proxy and Git clone the large files.
git clone git@github.com:{YOUR-USERNAME}/{YOUR-REPOSITORY}.git
Verify large files download with Dragonfly
Execute the command:
# find pods
kubectl -n dragonfly-system get pod -l component=dfdaemon
# find logs
pod_name=dfdaemon-xxxxx
kubectl -n dragonfly-system exec -it ${pod_name} -- grep "peer task done" /var/log/dragonfly/daemon/core.log
Example output:
2023-12-21T16:55:20.495+0800INFOpeer/peertask_conductor.go:1326peer task done, cost: 2238ms{"peer": "30.54.146.131-15874-f6729352-950e-412f-b876-0e5c8e3232b1", "task": "70c644474b6c986e3af27d742d3602469e88f8956956817f9f67082c6967dc1a", "component": "PeerTask", "trace": "35c801b7dac36eeb0ea43a58d1c82e77"}
Performance testing
Test the performance of single-machine large files download after the integration of Git LFS and Dragonfly P2P. Due to the influence of the network environment of the machine itself, the actual download time is not important, but the ratio of the increase in the download time in different scenarios is very important.
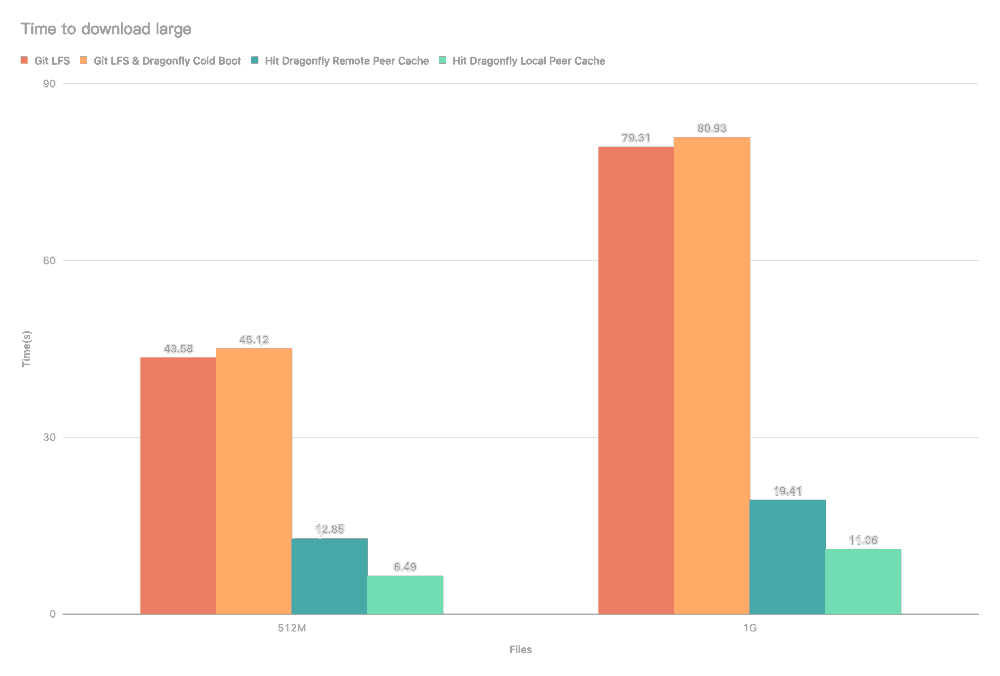
- Git LFS: Use Git LFS to download large files directly.
- Git LFS & Dragonfly Cold Boot: Use Git LFS to download large files via Dragonfly P2P network and no cache hits.
- Hit Dragonfly Remote Peer Cache: Use Git LFS to download large files via Dragonfly P2P network and hit the remote peer cache.
- Hit Dragonfly Remote Local Cache: Use Git LFS to download large files via Dragonfly P2P network and hit the local peer cache.
Test results show Git LFS and Dragonfly P2P integration. It can effectively reduce the file download time. Note that this test was a single-machine test, which means that in the case of cache hits, the performance limitation is on the disk. If Dragonfly is deployed on multiple machines for P2P download, the large files download speed will be faster.
Links
Dragonfly community
- Website: https://d7y.io/
- Github Repo: https://github.com/dragonflyoss/Dragonfly2
- Slack Channel: #dragonfly on CNCF Slack
- Discussion Group: dragonfly-discuss@googlegroups.com
- Twitter: @dragonfly_oss
Git LFS
- Website: https://git-lfs.com/
- Github Repo: https://github.com/git-lfs/git-lfs
- Document: https://github.com/git-lfs/git-lfs/tree/main/docs